Bitcoin mining crossed a historic threshold in late 2025. According to a recent report from GoMining, the network has entered the ZetaHash era, with computing power exceeding 1 ZetaHash per second.
But while hashrate soared to record levels, miner profitability went in the opposite direction. As a result, the mining industry will be larger, more industrialized, and more exposed to price risk than at any point in this cycle.
Bitcoin mining has entered a new regime.
In our 2025 Bitcoin Mining Market Review, we investigate:
🔹 How has the mining economy changed over the years?
🔹 What Relentless Hash Price Pressure Reveals About the Sector
🔹Why scale, power strategy, and capital structure are more important than cycles now… pic.twitter.com/bh5GJM5WaE— GoMining Institutional (@GoMiningInst) January 28, 2026
Hash rate reaches record high as mining scale expands
This report shows that Bitcoin’s network has been maintained for a long time 1 ZH/s on average for 7 daysindicating a structural change rather than a temporary spike.
This growth reflects aggressive hardware upgrades, new data centers, and expansion of industrial operations. Mining is no longer dominated by marginal players. It now resembles energy infrastructure.
As a result, competition for block rewards is increasing.
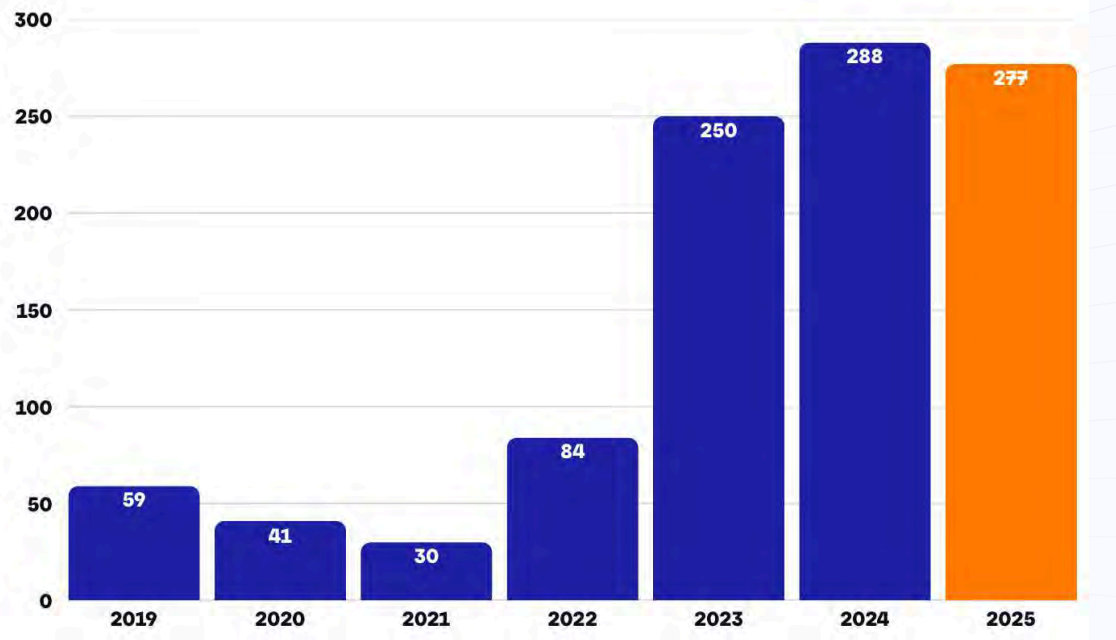
Annual increase in network hashrate. Source: GoMining
Despite network growth, revenue per miner is decreasing
While hashrate expands, Revenue per unit of compute fell into one of the narrowest ranges on record.
The report highlights that Miners’ incomes increasingly depend on bitcoin price and the difficulty of being alone. Other buffers, such as rising transaction fees and higher block subsidies that once cushioned margin pressure, are also fading.
This compression means that miners operate on thinner margins even though they are putting in more capital and power.
According to GoMining, the impact was seen in Menpur. For the first time since April 2023, Bitcoin’s memory pool was completely cleared multiple times in 2025.
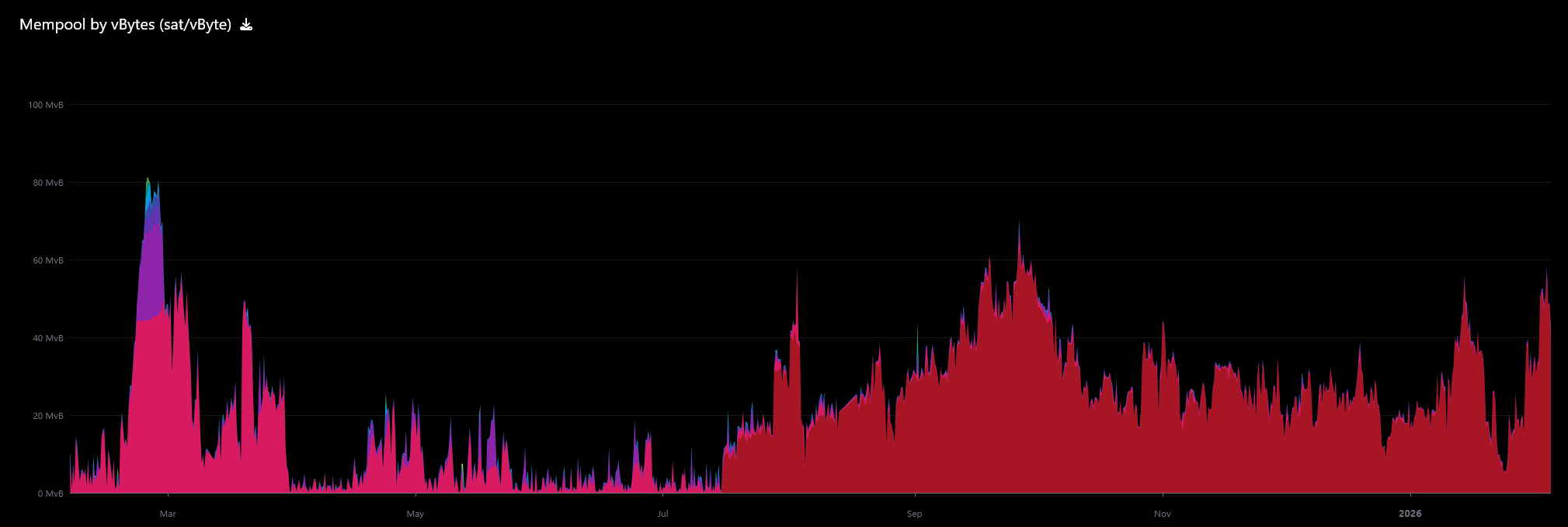
Mempool was cleared multiple times in 2025. Source: Mempool.space
This means that the Bitcoin network was so quiet that transactions were settled quickly, even with the lowest possible fees.
As a result, miners received almost nothing from fees and had to rely almost entirely on the price of Bitcoin and block subsidies for their income.
Transaction fees will hardly be reduced after the halving
The pressure worsened due to the post-half-life situation.
With the block subsidy reduced, 3.125 $BTCtrading fees could not offset the loss in revenue. The report notes that the fees are structured as follows: Less than 1% of total block reward for most of 2025.
As a result, the miner’s economy became directly exposed to Bitcoin price fluctuations, reducing internal stabilizing measures.
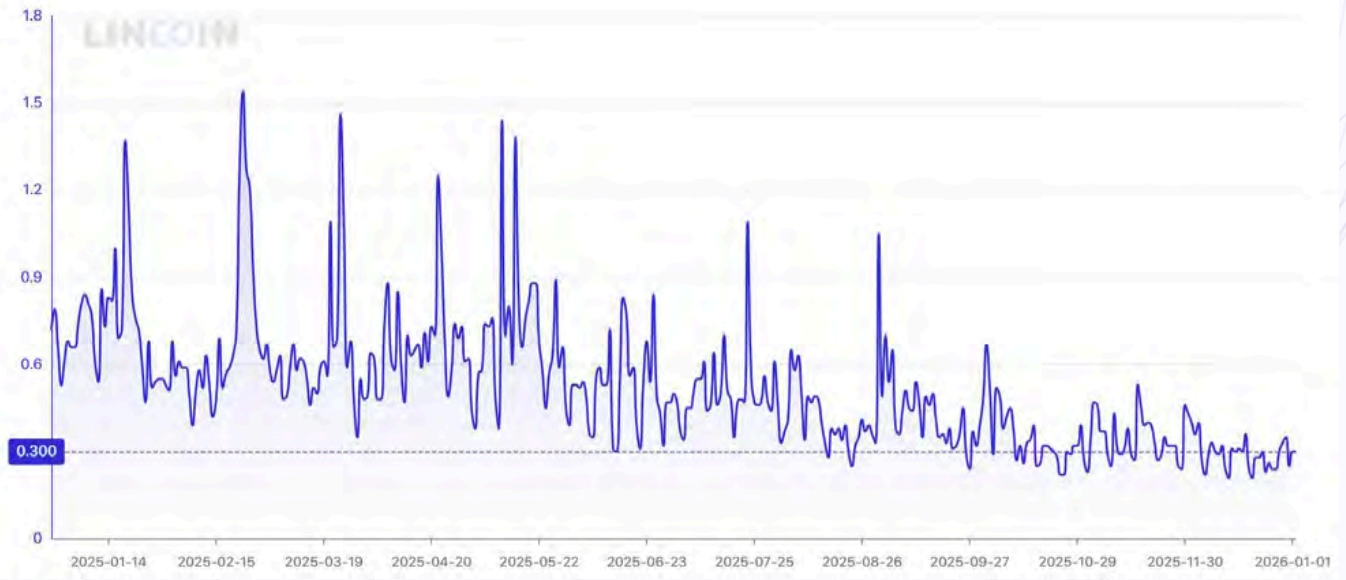
Throughout 2025, transaction fees accounted for less than 1% of total block rewards. Source: GoMining
Hashprice hits lows as profit margins continue to come under pressure
This squeeze was clearly visible in the hashprice, or the daily revenue earned per unit of hashrate.
According to reports, hash price has fallen to near all-time lows $35 per day per PH in November The decline continued into the end of the year. Finished the quarter near $38This is well below the historical average.
This leaves little room for operational error.
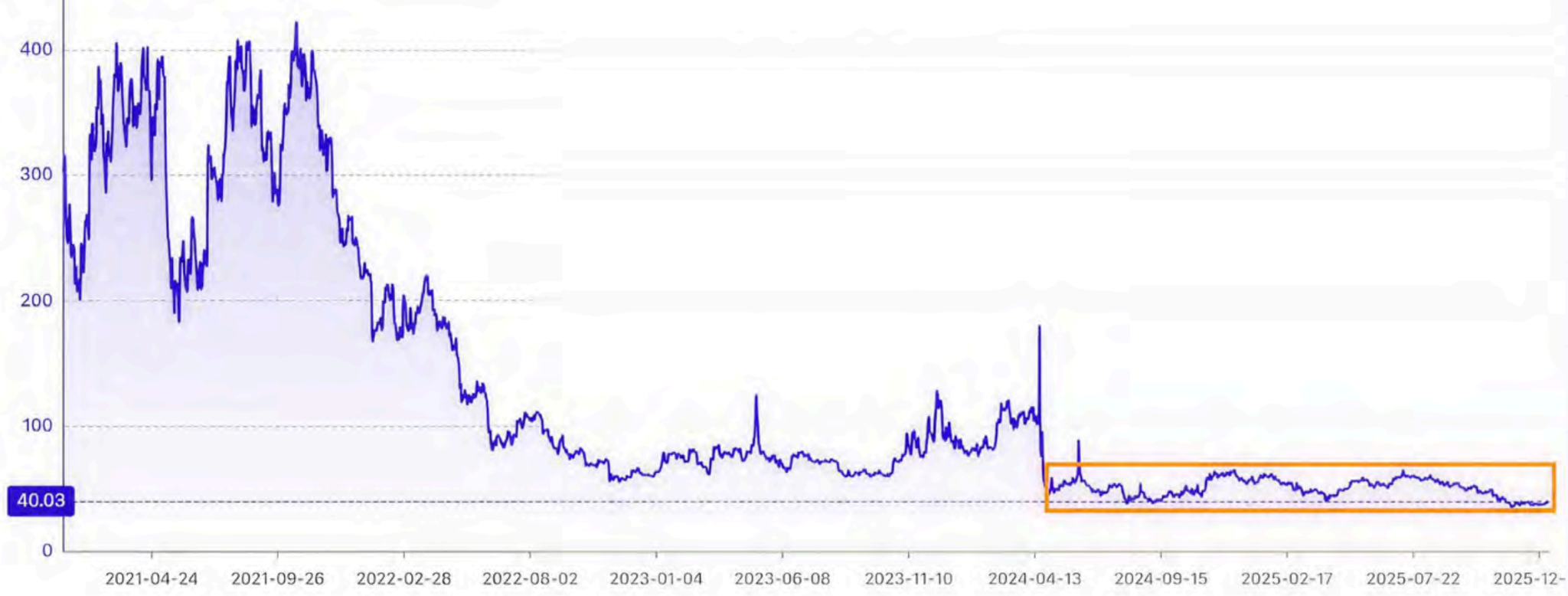
Bitcoin hash prices have continued to fall over the past year. Source: GoMining
Shutdown prices turn price levels into economic triggers
These findings are in close agreement with recent data on. Miner shutdown price.
With the current difficulties and electricity costs, $0.08 per kWhwidely used S21 series miners are close to breaking even at between $69,000 and $74,000 per transaction. $BTC. Below this range, many businesses stop generating operating profits.
More efficient high-end machines are still viable at much lower prices. But mid-level minors face immediate pressure.
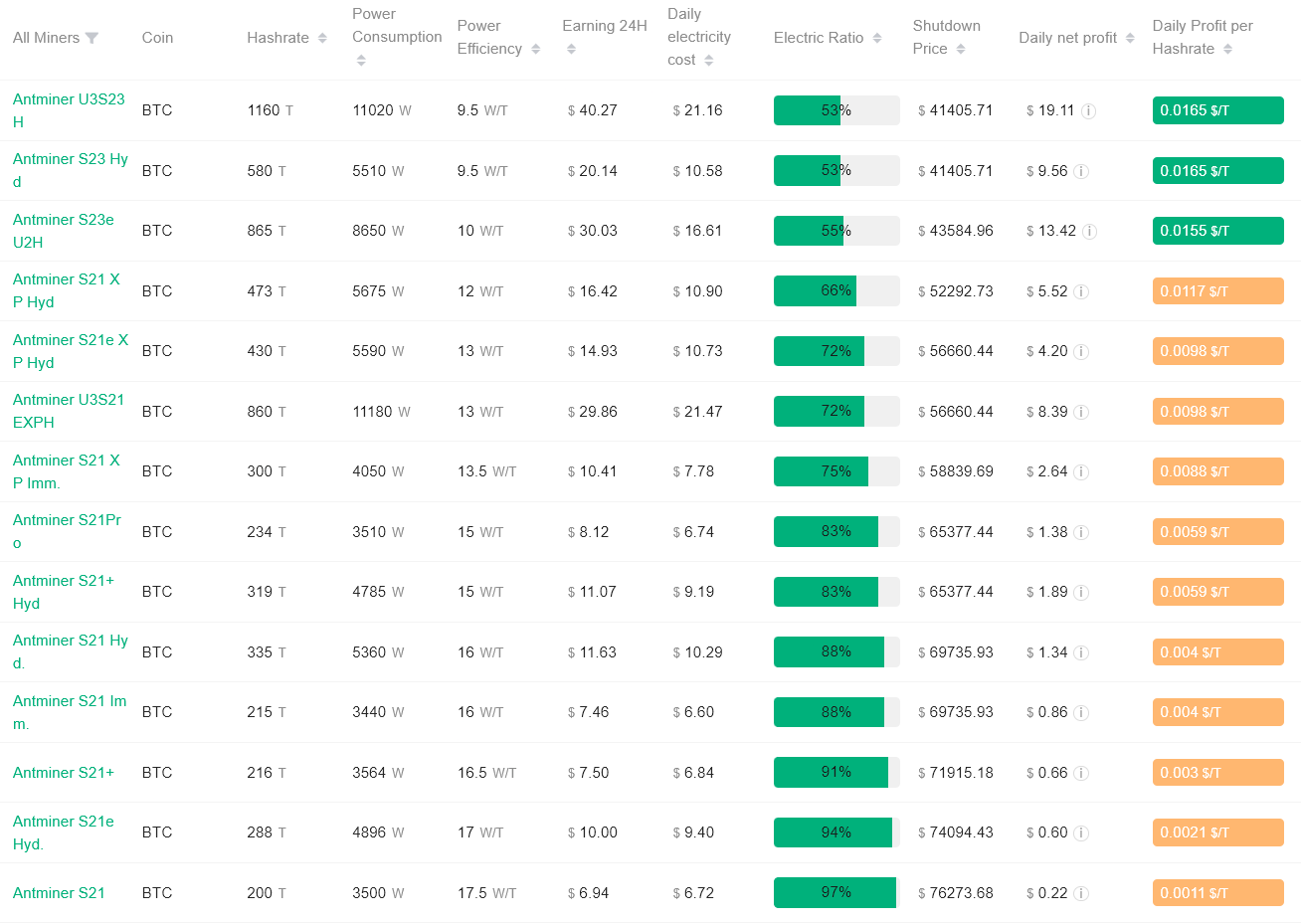
Most Bitcoin miners have a shutdown price of less than $70,000. Source: Antpur
Why this is important for Bitcoin price right now
This does not create a price floor. The market may trade below the break-even point for mining.
However, it creates behavioral threshold. If Bitcoin falls below a key stop level, weaker miners may sell reserves, shut down equipment, or reduce exposure.
Such actions could increase volatility in a market already strained by tight liquidity.
Bitcoin mining is more powerful and industrial than ever before. However, that scale comes with sensitivity. As hashrate increases and fees decrease, Price is more important, not lessfor minor stability.
It makes the level like this $70,000 It makes economic sense not because the graph says so, but because the cost structure of the network says so.
The article “Bitcoin mining enters the ZetaHash era as profitability tightens” was first published on BeInCrypto.


