Ethereum’s Fusaka upgrade has been enabled on the Sepolia testnet, marking the next big step in the network’s continued efforts to improve scalability and performance.
This upgrade marks the second phase of a three-phase rollout under Ethereum’s Fusaka roadmap, following the activation of the Holesky testnet on October 1st. Deployment of Sepolia supports network new src=”https://www.youtube.com/embed/haInlj7rTSs?start=” Frameborder=”0″ allowed=”accelerometer; autoplay; encrypted media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture”allowfullscreenloading=”lazy”>
Peer Data Availability Sampling (PeerDAS) is also being tested because larger blocks mean nodes are processing and storing more data.
PeerDAS allows Ethereum validators to validate transaction data by sampling small pieces from multiple peers instead of downloading everything, increasing speed and scalability while maintaining decentralization.
Paul Harris, another Fusaka core developer and protocol engineer for Consensys’ Teku client, said PeerDAS eliminates the need for validators to store all network data, greatly reducing the burden on nodes.
“Fusaka changes the way data is available and allows us to scale beyond what was possible before PeerDAS,” said Harris.
The Ethereum Foundation announced the Fusaka testnet schedule on September 26th, outlining the final steps before the network’s next major upgrade. Fusaka follows this year’s Pectra update, with the final Hoodi testnet trial set for October 28th and mainnet launch scheduled for December.
Related: Ethereum bulls tout supercycle, but Wall Street is skeptical
A brief history of Ethereum upgrades
Since its launch in July 2015, the Ethereum network has undergone several major upgrades to improve scalability, security, and performance.
The most recent review was conducted on May 7, when the Pectra upgrade was published and introduced three major improvement suggestions. Among the changes, Pectra now allows externally owned accounts to function like smart contracts and pay gas fees with tokens other than ETH, and increased the staking limit for validators from 32 ETH to 2,048 ETH. This upgrade also expands the number of data blobs allowed per block.
Prior to Pectra, Ethereum rolled out the Dencun upgrade on March 13, 2024, significantly reducing the cost of gas fees within the network. Within a year of the Dencun upgrade, Ethereum’s average gas price dropped by 95%.
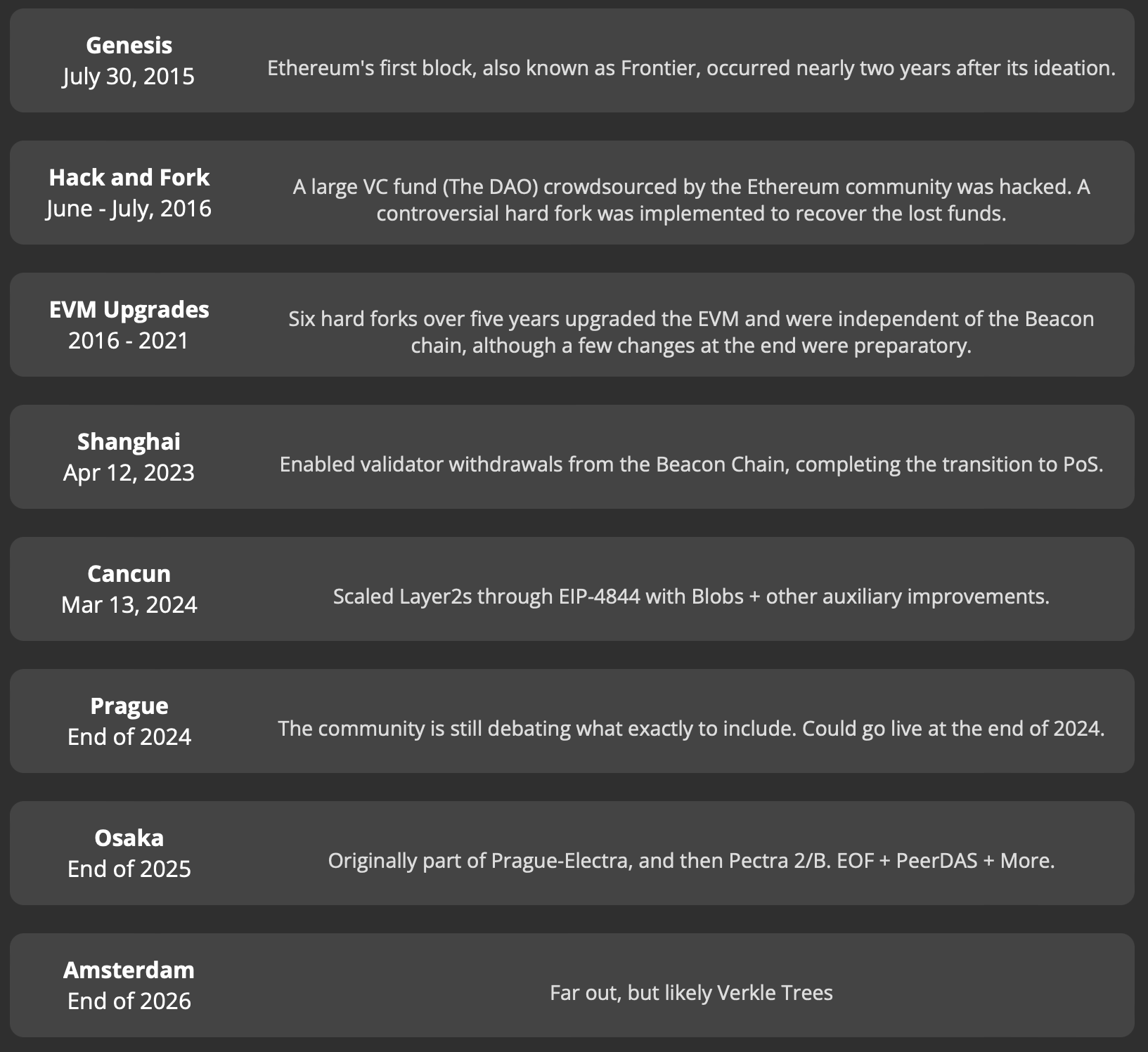
Ethereum hard fork timeline. sauce: ethroadmap.com
Perhaps the most famous Ethereum upgrade is known as the Merge, which occurred in September 2022 and moved Ethereum from a proof-of-work blockchain to a proof-of-stake blockchain.
This merger ended mining, introduced validators, and reduced energy costs by up to 99%.
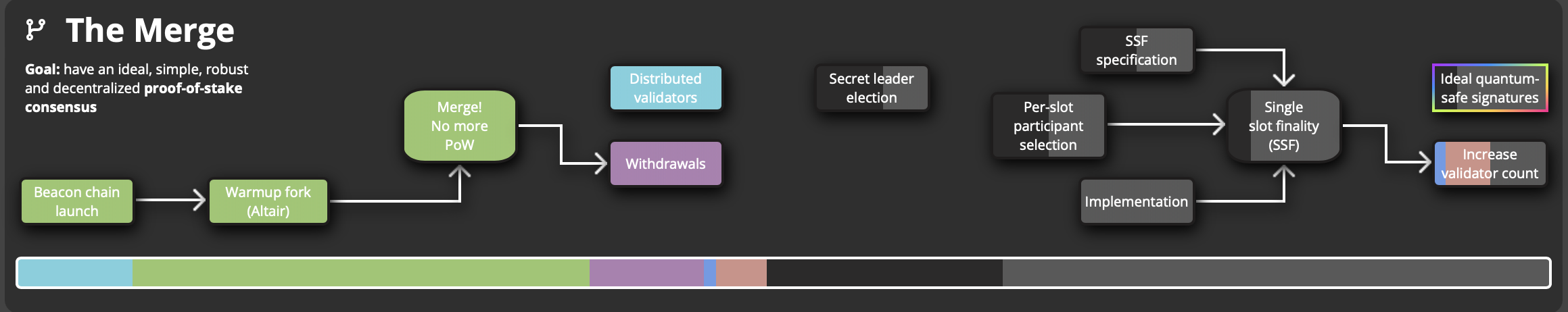
merge. sauce: ethroadmap.com
The April 2023 Shanghai Upgrade was also an important step in the network’s roadmap, as it enabled withdrawals for the first time for validators staking Ether (ETH), completing Ethereum’s transition to proof-of-stake.
magazine: Asia Express: Alibaba founder’s push for Ethereum, whales occupy 91% of Korean market