Ethereum consensus client Prism said its validators missed out on 382 ETH, worth more than $1 million, due to a software bug that caused a network outage shortly after a recent Fusaka upgrade.
The incident, detailed in a post-mortem titled “Fusaka Mainnet Prysm Incident,” resulted from a resource exhaustion event that affected nearly all Prysm nodes and led to blocking and missing authentication.
What causes Prysm to stop?
Offchain Labs, the developer of Prysm, said the issue started on December 4 and was caused by a previously introduced bug that caused delays in validator requests.
These delays resulted in blocks and lost authentication across the network.
“Prysm beacon nodes received certificates from nodes that may be out of sync with the network. These certificates referenced block roots from a previous epoch,” the project explained.
This interruption resulted in the loss of 41 epochs and 248 blocks out of 1,344 available slots. This corresponds to a missed slot rate of 18.5%, and the overall network participation rate during the incident dropped to 75%.
According to Offchain Labs, the bug causing this behavior was introduced about a month ago, deployed to the testnet, and occurred on the mainnet after a Fusaka upgrade.
Prysm said that while temporary mitigation measures reduced the immediate impact, it has since introduced permanent changes to its authentication validation logic to prevent it from happening again.
Diversity of Ethereum clients
Meanwhile, the recent outage has brought renewed scrutiny to the risks posed by Ethereum’s customer concentration and software monoculture.
Offchain Labs said the outage could have had more severe consequences had Prysm held a larger share of Ethereum’s validator base. The company pointed to Ethereum’s client diversity as a key factor in preventing widespread network failures.
“Clients with more than 1/3 of the network may cause a temporary loss of finality and more missing blocks. Bug clients with more than 2/3 may finalize invalid chains.”
Despite these mitigating measures, the incident has reinforced calls for greater customer diversity.
According to data from Miga Labs, Lighthouse remains the leading Ethereum consensus client, accounting for 51.39% of validators. Prysm accounts for 19.06%, followed by Teku with 13.71% and Nimbus with 9.25%.
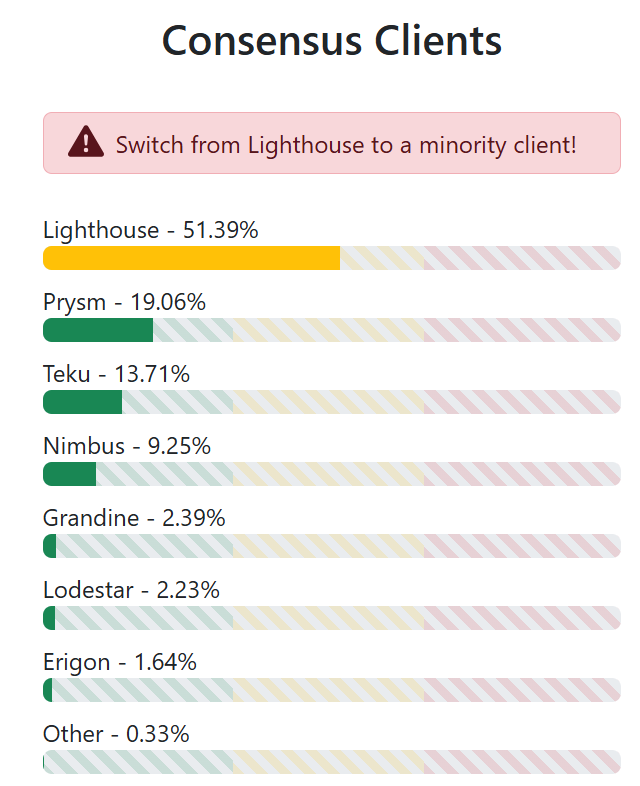
Ethereum consensus client. Source: Client Diversity
Lighthouse’s share is roughly 15 percentage points off the threshold of what some researchers consider systemic risk.
As a result, developers and ecosystem participants have once again urged validators to consider switching to alternative clients to reduce the likelihood that a single software flaw will disrupt core blockchain operations.
The post Prysm Bug Cost Ethereum Validators Over $1 Million After Fusaka Upgrade first appeared on BeInCrypto.


